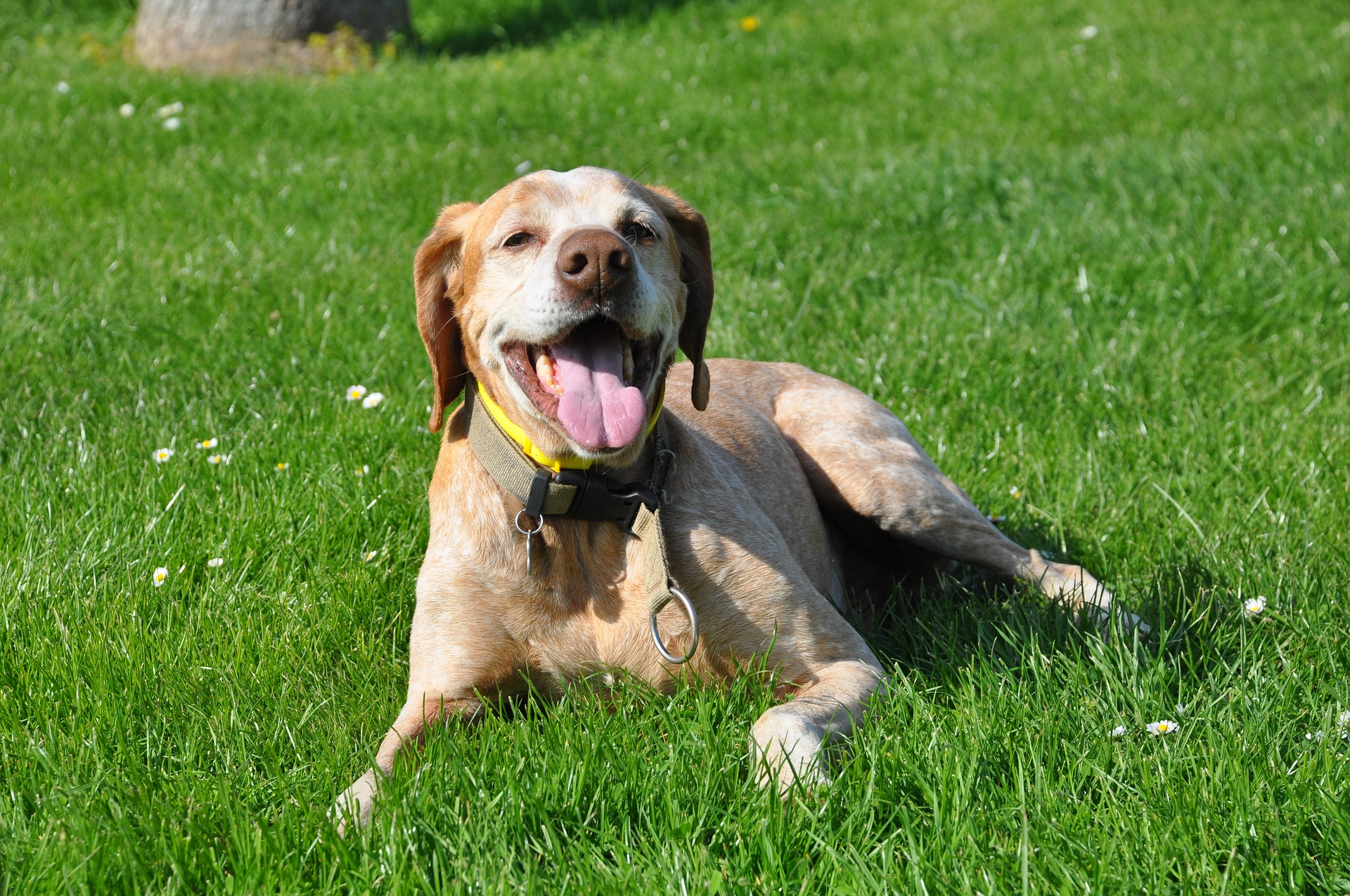
Dog body language gives off important cues on a dog’s emotion and intentions. Being able to read your dog’s body language accurately constitutes an important step towards effectively communicating with your dog. Below tips may help you understand your canine better.
Tail Held High: When a dog holds its tail high, it often signals high arousal and the possibility of aggressive behavior. An agitated and aggressive dog may also flick its tail back and forth vigorously.
In a relaxed state, a dog is more likely to carry its tail in a neutral position, extended out behind it.
Wagging of Tail: When dogs wag their tails, they wag loosely back and forth at a medium height. It would mean that they are being friendly. It could also mean they are feeling excitement.
Closed Mouth: Relaxed dogs may have closed or partially open mouths. When a dog is feeling tense, they will tightly close their mouths, and yawning or panting heavily could indicate stress.
Ears Up for Greeting: One sign of a friendly dog is that its ears move back just slightly. A submissive dog will move its ears even further back as an appeasement gesture. Dogs with erectly pricked ears may signify that they are ready to stand their ground against another animal if necessary – but this behavior is specific to individual dogs.
Turning to the side: Dogs may turn their bodies to the side to shut off a potential threat. When dogs turn to their side, it could mean that they are trying to show that they mean no harm.
Raised Hackles: When dogs are feeling frightened or overstimulated, the hair on their back and tails will fluff out and stand on end. It may also indicate that they are ready to react.
Pupil dilation and blinking: A dog’s pupil dilate when they are afraid or are getting ready to attack. They could feel fearful or aggressive. However, dilation of pupils can also indicate high arousal. Eye blinks could indicate desire for a peaceful greeting, while direct eye contact without blinking or looking away can signal a challenge.
Compacted Body: When a dog is afraid of something, its body may appear as small as possible. Usually with its head held low. If a dog curls its tails underneath its bodies, it may also indicate extreme fear.
Whiskers Stiffened: When dogs are stimulated by something and are about to react, their whiskers are more likely to stiffen and extend outward.
Panting: When dogs pant, it could indicate various things. Sometimes, it means they feel stressed or frightened. However, panting usually helps them to cool down because they are unable to sweat like humans do.
Yawning: Dogs’ yawning sometimes indicates that they are stressed. However, it can also be a form of communication between other animals. Oftentimes, when a dog is facing an aggressive threat, they might offer a yawn to show that they are not interested in any sort of conflict.