One way to understand more about your cat’s emotions and wellbeing is to look into their body language. Not sure what your cat means? Go through the list below to better interpret what your cat’s body language might be telling you.
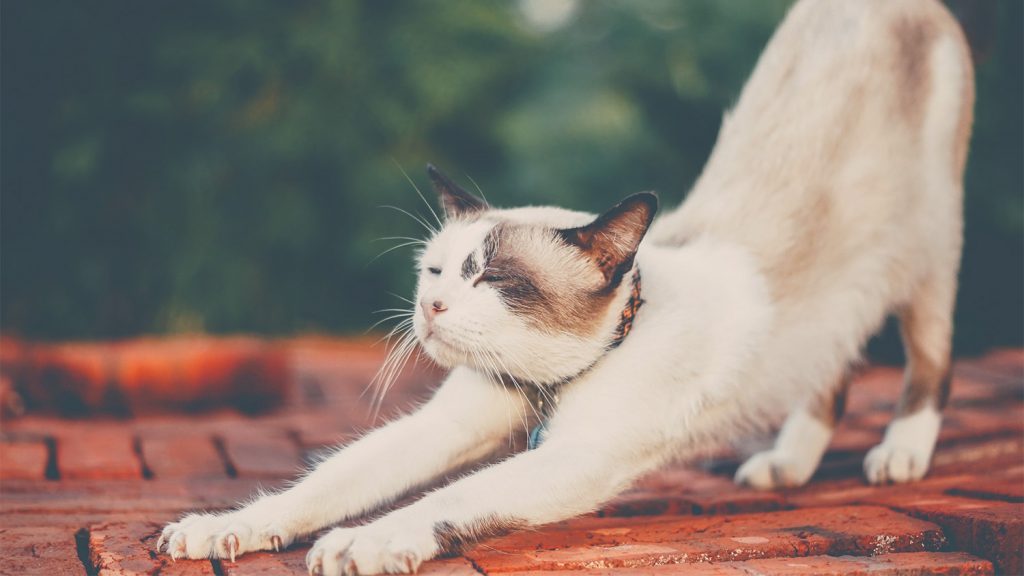
Tail held high: When a cat holds its tail high, it can signal that it is friendly and relaxed. The higher the cat’s tail, the more confident it may be.
However, if its tail raises high with fur erect and puffed out, it usually indicates alarm or potential aggression. As it becomes more unsure or fearful, its tail is more likely to slink lower.
Wagging of tail: When a cat’s tail begins to wag back and forth, it would mean that an unfriendly encounter or predatory attack is about to occur.
Closed mouth: For cats, they have closed mouths when they are relaxed.
Ears up for greeting: Confident cats will normally hold their ears forward and alert when greeting people. If their ears move backwards or twitch, it may indicate that they are feeling uncertainty or that an encounter is not going well.
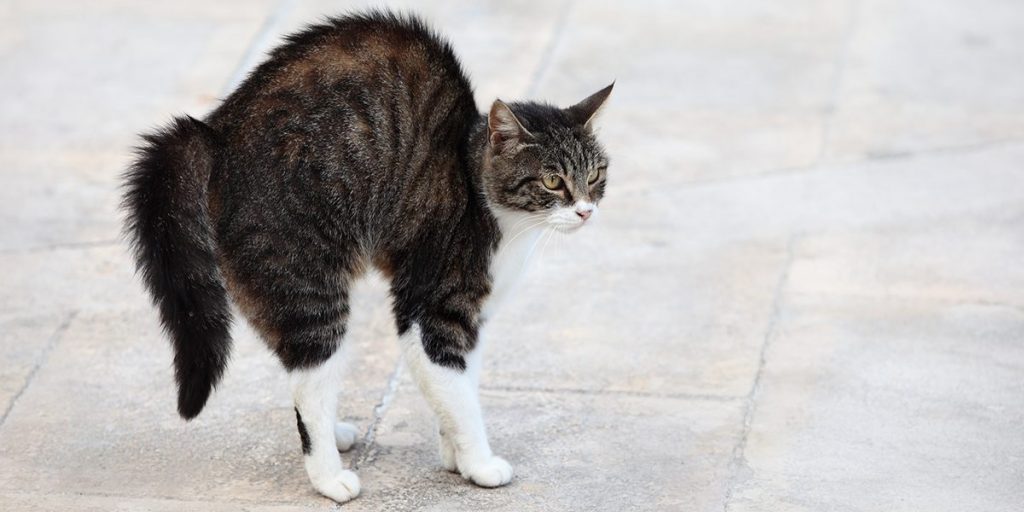
Turning to the side: Cats may turn their bodies to their side when attempting to shut off a potential threat. They do this to appear larger and more threatening to their opponent.
Lying belly up: When cats are lying down with their belly up, they usually do so in self-defense. This position allows them to have all four paws with claws drawn, ready to react to any threat.
However sometimes, cats may lie on their backs for people they are close to, but do not rub their bellies! Very few cats enjoy having their bellies rubbed and may respond aggressively.
Raised Hackles: When a cat feels frightened or overstimulated, the hair on their back and tails fluffs and stands on end. Usually, this would mean that they are ready to react.
Pupil Dilation and Blinking: Cats’ pupils dilate when they are afraid or getting ready to attack. However, pupil dilation can also indicate high arousal in cats. Eye blinking indicates the desire for a peaceful greeting. If there is direct eye contact without blinking or looking away, it can signal a challenge in cats.
Compacted Body: When a cat is afraid of something, it will make its body appear as small as possible, usually with its head held low. If a cat curls its tails underneath its bodies, it could indicate that the cat is feeling extreme fear.
Whiskers Stiffened: Cats have a normal height and structure to their whiskers. If they are stimulated by something and are about to react, their whiskers are more likely to stiffen and extend outward.
Panting: Panting in cats could mean that they are highly stressed or frightened. However, if a cat is panting but it is not interacting with anyone or is not in a fearful situation, it could indicate a serious health condition. Bring your cat to a veterinarian immediately if this happens.
Yawning: Cats may yawn as a calming behavior in conflicting situations.