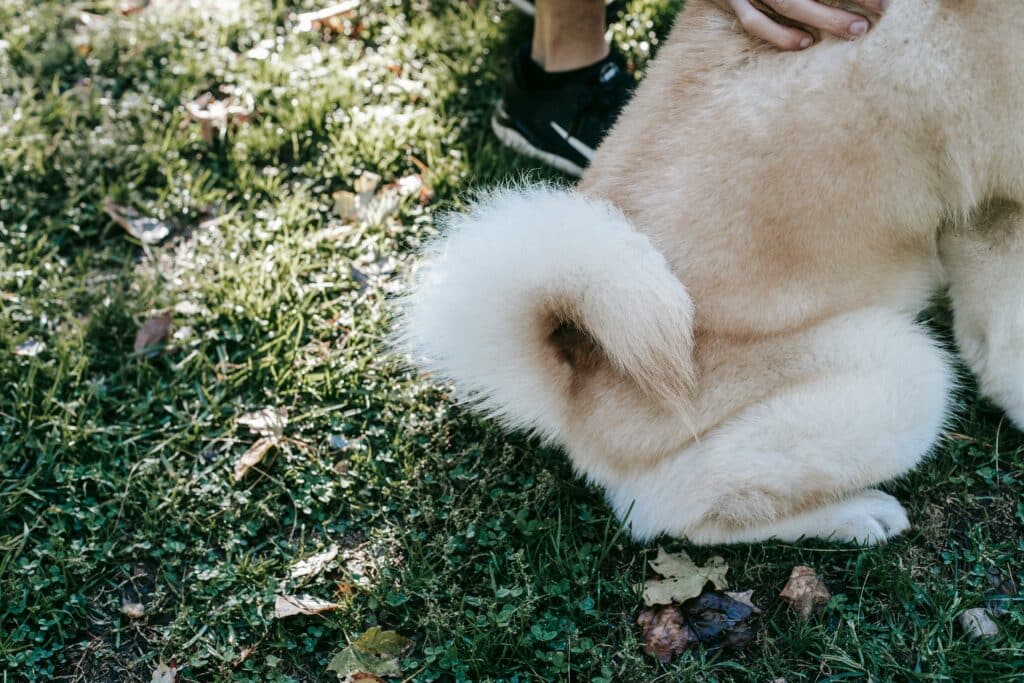
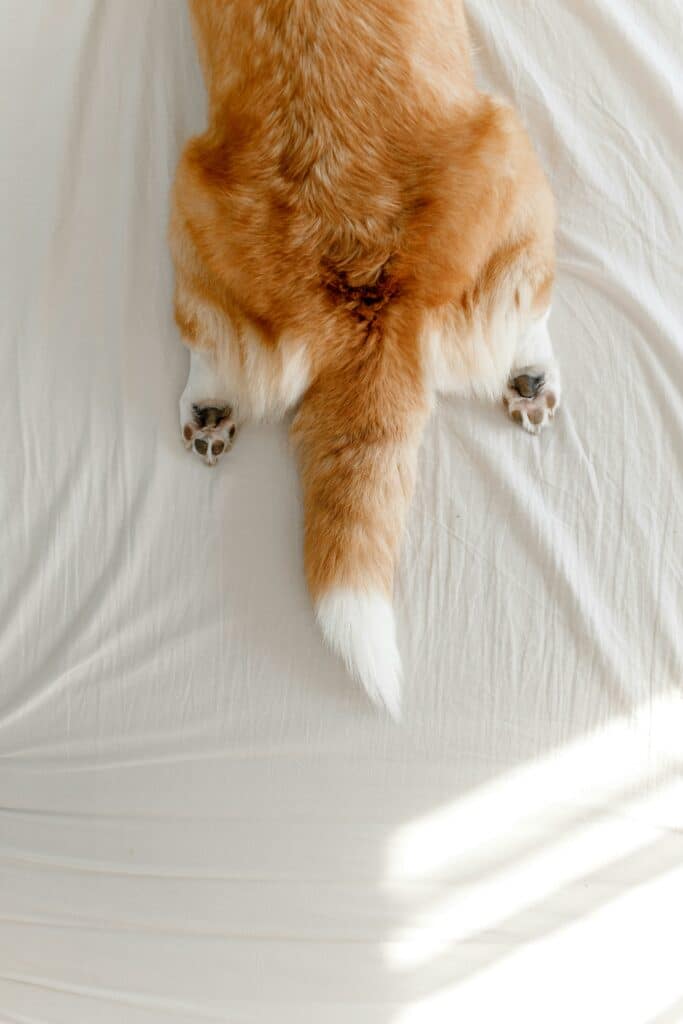
Dogs use their tails as a powerful form of nonverbal communication. While many assume a wagging tail always signals happiness, the reality is far more complex. Tail movements can indicate excitement, aggression, submission, and even uncertainty.
The Role of Tail Wagging in Canine Communication
Dogs rely on body language to communicate, and tail wagging plays a crucial role. The direction, speed, and height of the wag convey different messages:
Left vs. Right Wagging: Studies suggest that a wag to the right often indicates positive emotions, while a wag to the left may signal stress or fear.
Fast vs. Slow Wagging: A fast, enthusiastic wag is usually associated with joy, while slower, deliberate wags might mean hesitation.
High vs. Low Wagging: A high tail wag often signals dominance or confidence, whereas a low wag may indicate submission or anxiety.
The Science Behind Tail Wagging
The Brain’s Influence
Scientific studies reveal that tail wagging is linked to brain function. The left hemisphere of the brain controls positive emotions, causing right-side tail movements. Conversely, the right hemisphere governs negative emotions, leading to left-side wags.
Breed and Tail Shape Matter
Not all dogs communicate the same way. Breeds with curly tails, like Pugs, or dock-tailed breeds, like Australian Shepherds, may have different tail signals. Understanding these differences is essential for proper dog behavior interpretation.

Common Misconceptions About Dog Tail Wagging
1. A Wagging Tail Always Means a Happy Dog
A stiff, rapid wag with raised hackles could mean aggression.
A slow, hesitant wag can indicate uncertainty or nervousness.
2. Dogs Wag Their Tails Only for Humans
Dogs use tail wagging to communicate with other dogs.
A submissive dog may lower its tail and wag slightly to show deference.
3. Puppies Wag Their Tails at Birth
Newborn puppies do not wag their tails until they start social interactions at around 3-4 weeks old.
How to Interpret Your Dog's Tail Wagging
Context Matters
Understanding dog tail wagging requires observing the full body language. Signs such as ear positioning, facial expressions, and overall posture provide additional clues.
Situational Examples
| Tail Position | Wag Speed | Meaning |
|---|---|---|
| High & Stiff | Rapid | Alert/Aggressive |
| Mid-Level & Relaxed | Moderate | Friendly & Playful |
| Low & Tucked | Slow | Fearful or Submissive |
Enhancing Your Bond Through Tail Communication
Recognizing tail wag patterns helps improve dog-owner communication. By responding appropriately to tail signals, owners can strengthen trust and prevent behavioral misunderstandings.
Training Tip
Rewarding calm, neutral wagging with treats and praise reinforces positive social behaviors in dogs.

Conclusion
Dog tail wagging is more than just a sign of joy; it’s a sophisticated communication tool. By paying close attention to wag direction, speed, and position, owners can better understand their pet’s emotions and respond accordingly.
References
Dog Tail Signs: What’s Your Dog’s Tail Language? – https://www.whole-dog-journal.com/behavior/dog-tail-language/
Why Do Dogs Wag Their Tails? – https://www.petmd.com/dog/behavior/why-do-dogs-wag-their-tails?
Interpreting Tail Wags in Dogs – https://vcahospitals.com/know-your-pet/interpreting-tail-wags-in-dogs
Share this:
- Click to share on WhatsApp (Opens in new window) WhatsApp
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window) Facebook
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window) LinkedIn
- Click to share on Pinterest (Opens in new window) Pinterest
- Click to share on Tumblr (Opens in new window) Tumblr
- Click to share on X (Opens in new window) X
- Click to share on Reddit (Opens in new window) Reddit
- Click to share on Telegram (Opens in new window) Telegram
- Click to email a link to a friend (Opens in new window) Email
- Click to print (Opens in new window) Print