Bringing a pet into your home is a big decision, and choosing the right one requires careful consideration. If you’re interested in small pet care, you might be wondering whether a rabbit, hamster, or guinea pig is the best fit for your lifestyle. Each of these pets has unique needs, space requirements, and personality traits.
In this guide, we’ll compare rabbits, hamsters, and guinea pigs to help you determine which one suits you best. Whether you’re looking for a low-maintenance pet, a social companion, or a long-term furry friend, understanding their differences will ensure you make the right choice.

1. Space Requirements and Housing Needs
One of the first factors to consider when choosing a small pet is how much space you can provide. Each of these animals has different housing needs, ranging from compact enclosures to spacious play areas.
Rabbits: Room to Roam
Rabbits need plenty of space to move around. While some people keep them in hutches, it’s recommended to provide a large pen or a bunny-proofed room where they can roam freely.
- Minimum cage size: 12 square feet, with access to an exercise area.
- Ideal living conditions: Indoor or outdoor enclosures with protection from predators and weather.
- Essential additions: Litter box, hay feeder, and hideouts for resting.
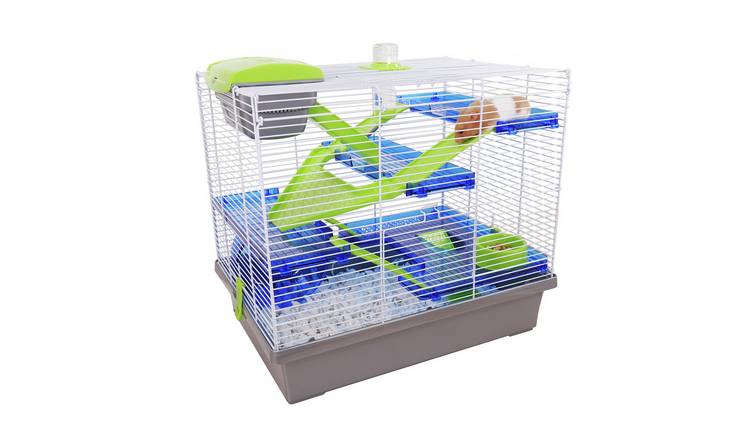
Hamsters: Compact and Cozy
If you’re looking for a small pet that doesn’t require much space, a hamster might be a great choice. These tiny creatures are perfectly happy in a well-designed cage with enough toys and tunnels for enrichment.
- Minimum cage size: 450 square inches of floor space.
- Ideal living conditions: A multi-level cage with bedding for burrowing.
- Essential additions: Exercise wheel, hideouts, chew toys, and food storage areas.
Guinea Pigs: Social but Space-Needy
Guinea pigs need more space than hamsters but less than rabbits. Since they’re highly social animals, they should always be housed in pairs or groups.
- Minimum cage size: 7.5 square feet per guinea pig.
- Ideal living conditions: A large enclosure with solid flooring (not wire-bottomed) to protect their feet.
- Essential additions: Hideouts, hay racks, tunnels, and a water bottle.

2. Temperament and Social Behavior
Choosing a pet isn’t just about space—it’s also about personality and social needs. Some pets are highly interactive, while others are more independent.
Rabbits: Intelligent but Reserved
Rabbits are smart and trainable but can be shy at first. They require gentle handling and time to build trust with their owners.
- Can be trained to use a litter box.
- Prefer gentle interactions; can get startled easily.
- Best suited for patient owners who can spend time bonding with them.
Hamsters: Solitary and Independent
Hamsters are territorial creatures that prefer living alone. Unlike rabbits and guinea pigs, they don’t crave social interaction.
- Most active at night (nocturnal behavior).
- May nip if woken up suddenly.
- Great for people who prefer an independent pet.
Guinea Pigs: Friendly and Social
Guinea pigs are very social animals that thrive when kept in pairs or small groups. They love interacting with their owners and often respond to their names.
- Communicate through squeaks and purring sounds.
- Rarely bite and are very gentle.
- Perfect for families and first-time pet owners.

3. Lifespan and Commitment
Before adopting any pet, consider how long they live and whether you’re ready for that commitment.
| Pet Type | Average Lifespan | Commitment Level |
|---|---|---|
| Rabbits | 8-12 years | High |
| Hamsters | 2-3 years | Low |
| Guinea Pigs | 5-7 years | Moderate |
If you want a long-term companion, a rabbit might be ideal. If you prefer a shorter commitment, a hamster is a better choice.
4. Diet and Nutrition
Each pet has different dietary needs, and providing the right nutrition is essential for small pet care.
Rabbits: High-Fiber Diet
- Main food: Hay (80% of diet).
- Supplements: Leafy greens and pellets.
- Avoid: Sugary treats and iceberg lettuce.
Hamsters: Omnivorous but Small Eaters
- Main food: Pellets or a seed mix.
- Occasional treats: Fruits, vegetables, and mealworms.
- Avoid: Citrus fruits and chocolate.
Guinea Pigs: Vitamin C Is Essential
- Main food: Hay and fresh vegetables.
- Supplements: Vitamin C-enriched pellets.
- Avoid: Onions, garlic, and dairy products.

5. Maintenance and Grooming
Some pets require regular grooming, while others are more self-sufficient.
Rabbits: Regular Grooming Required
- Long-haired breeds need daily brushing.
- Nails should be trimmed monthly.
- Litter box should be cleaned often.
Hamsters: Low Maintenance but Messy
- Self-grooming but need weekly cage cleaning.
- Deep cleaning required every few weeks.
Guinea Pigs: Moderate Grooming Needs
- Short-haired breeds need weekly brushing.
- Long-haired breeds need daily grooming.
- Cage cleaning required 2-3 times a week.
Final Thoughts: Which Small Pet Is Right for You?
Choosing between rabbits, hamsters, and guinea pigs depends on your lifestyle, space, and commitment level.
- Pick a rabbit if you want a long-term, intelligent pet with space to roam.
- Pick a hamster if you need a low-maintenance, independent pet.
- Pick a guinea pig if you want a social, family-friendly companion.
No matter which pet you choose, understanding small pet care will help you provide the best life for your new furry friend!
References
Rabbit vs Guinea Pig. Which pet should I get? – https://guineadad.com/blogs/news/rabbit-vs-guinea-pig-which-pet-should-i-get-with-infographic?srsltid=AfmBOopY6LqEIyOsPjquQOkpjodG-IbfUHNK6b-WpBKZ_a84wj3bKQ4y&
Hamsters – RSPCA – https://www.rspca.org.uk/adviceandwelfare/pets/rodents/hamsters
Guinea Pigs vs. Hamsters: Which Pet Is Right for You? – https://be.chewy.com/guinea-pig-vs-hamster/