Housing rabbits and guinea pigs together has been a common practice among pet owners seeking to provide companionship for their small animals. However, it’s crucial to understand the implications of such cohabitation to ensure the health and well-being of both species. This article explores the pros and cons of keeping rabbits and guinea pigs together and offers best practices for their care.
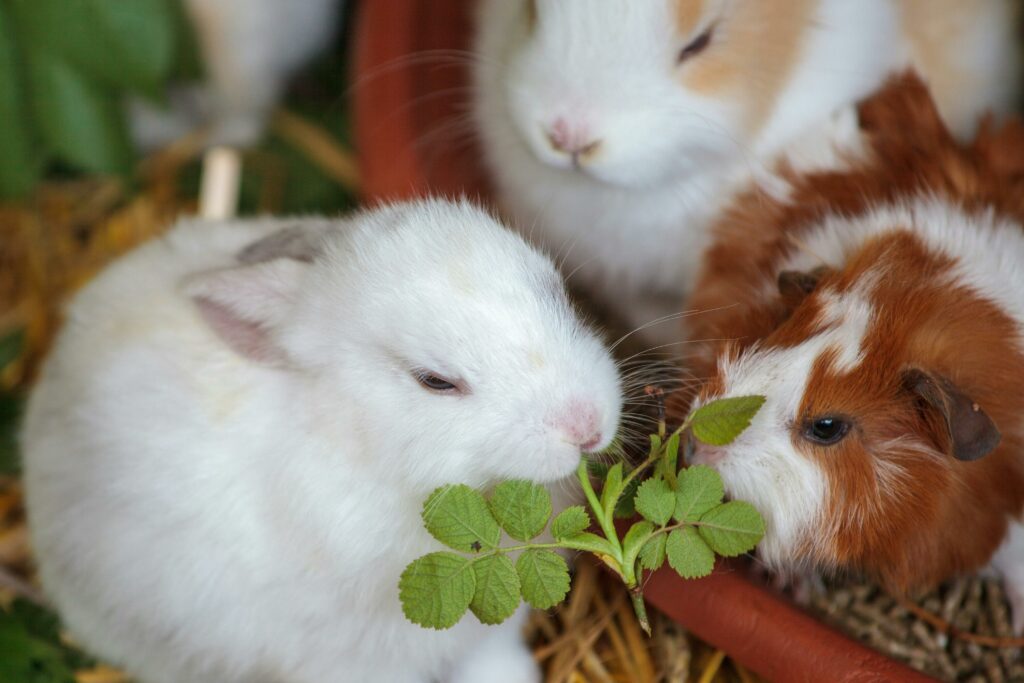

Pros of Housing Rabbits and Guinea Pigs Together
Historically, rabbits and guinea pigs were often housed together, primarily due to the lack of safe neutering options for rabbits. This arrangement was believed to offer companionship to both species, especially when neutering was not feasible. However, with advancements in veterinary care, neutering rabbits has become routine, allowing them to be paired with their own kind. While some pet owners have observed harmonious relationships between individual rabbits and guinea pigs, these cases are exceptions rather than the norm.
Cons of Housing Rabbits and Guinea Pigs Together
Despite occasional successful cohabitation, several significant concerns arise when keeping rabbits and guinea pigs in the same enclosure:
1. Communication Differences
Rabbits and guinea pigs have distinct communication methods. Rabbits use body language such as thumping, grooming, and specific postures to convey their feelings, while guinea pigs rely on vocalizations and subtle movements. This disparity can lead to misunderstandings and stress for both animals. Their differing communication styles can result in conflicts and even fights.
2. Dietary Requirements
The nutritional needs of rabbits and guinea pigs differ notably. Guinea pigs cannot synthesize vitamin C and require a diet rich in this nutrient, whereas rabbits do not have this requirement. Feeding them the same diet can lead to deficiencies in guinea pigs and potential health issues in rabbits. Their differing dietary needs make cohabitation challenging.
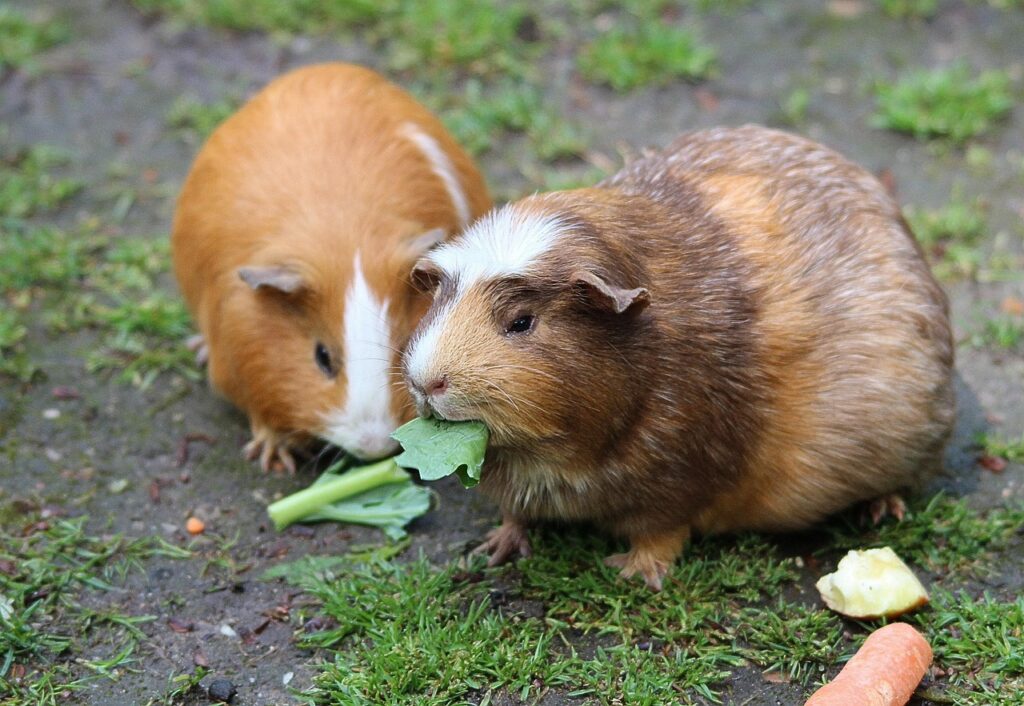

3. Risk of Injury
Rabbits are generally larger and stronger than guinea pigs. Their powerful hind legs can unintentionally cause serious injuries to guinea pigs, especially during play or if startled. Rabbits may injure guinea pigs, either intentionally or unintentionally, posing a significant risk.
4. Disease Transmission
Rabbits can carry the bacterium Bordetella bronchiseptica, which is harmless to them but can cause severe respiratory infections in guinea pigs. This risk underscores the potential health hazards of housing these species together. The Bunnyjackpot Foundation highlights the danger of disease transmission between rabbits and guinea pigs.
5. Social Needs
Both rabbits and guinea pigs are social animals that thrive in the company of their own species. Housing them together does not fulfill their social requirements and can lead to loneliness and behavioral issues. The PDSA advises that rabbits should be kept with other rabbits, and guinea pigs with other guinea pigs, to meet their social needs.
Best Practices for Keeping Rabbits and Guinea Pigs
Considering the potential risks and challenges, it’s advisable to house rabbits and guinea pigs separately. Here are some best practices to ensure their well-being:
1. Provide Species-Specific Companionship
Ensure that both rabbits and guinea pigs have companions of their own species. This arrangement allows them to engage in natural behaviors and communication, promoting mental and emotional health.
2. Separate Living Quarters
Maintain separate enclosures for rabbits and guinea pigs, tailored to their specific needs. This approach prevents potential injuries and reduces stress associated with interspecies cohabitation.
3. Dietary Management
Feed rabbits and guinea pigs diets formulated for their unique nutritional requirements. This practice ensures they receive the necessary nutrients without the risk of deficiencies or health issues.
4. Veterinary Care
Schedule regular veterinary check-ups for both rabbits and guinea pigs to monitor their health and address any concerns promptly.
5. Enrichment and Socialization
Provide ample enrichment opportunities and social interaction for both species. This includes toys, hiding spots, and safe spaces to explore, enhancing their quality of life.

Conclusion
While the idea of housing rabbits and guinea pigs together may seem appealing, the differences in their communication, dietary needs, physical characteristics, and susceptibility to diseases make cohabitation inadvisable. To ensure the health and happiness of both species, it’s best to provide separate living arrangements and companionship of their own kind.
References
Vet Q&A: Can I keep rabbits with guinea pigs? – https://www.pdsa.org.uk/what-we-do/blog/vet-qa-can-i-keep-rabbits-with-guinea-pigs?
Can rabbits and guinea pigs live together? – https://bunnyjackpotfoundation.co.uk/guidance/can-guineapigs-rabbits-live-together?
Share this:
- Click to share on WhatsApp (Opens in new window) WhatsApp
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window) Facebook
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window) LinkedIn
- Click to share on Pinterest (Opens in new window) Pinterest
- Click to share on Tumblr (Opens in new window) Tumblr
- Click to share on X (Opens in new window) X
- Click to share on Reddit (Opens in new window) Reddit
- Click to share on Telegram (Opens in new window) Telegram
- Click to email a link to a friend (Opens in new window) Email
- Click to print (Opens in new window) Print