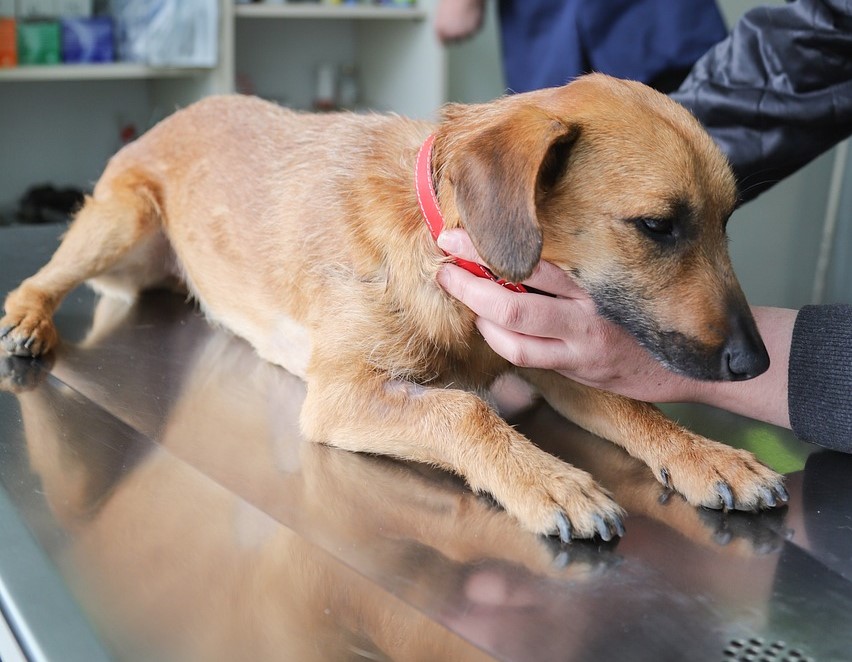
Welcome to our blog post, where we delve into the significance of dog vaccinations and how they contribute to the overall well-being and disease prevention of our beloved furry friends. As responsible pet owners, it’s crucial to understand the role vaccinations play in safeguarding our dogs from harmful diseases. By staying informed and proactive about vaccinations, we can ensure a long, healthy, and happy life for our canine companions.
The Basics of Vaccinations
Vaccinations are essential medical interventions that stimulate the immune system to recognize and fight off specific diseases. They work by introducing harmless versions of pathogens, allowing the immune system to develop a defence mechanism. Core vaccines are recommended for all dogs as they protect against common and severe diseases, while non-core vaccines are based on individual risk factors and lifestyle.
Core Vaccines for Dogs
A core vaccine is essential for all dogs as it protects against highly contagious and potentially life-threatening diseases. These vaccines target pathogens such as rabies, distemper, parvovirus, and hepatitis, which are prevalent and pose significant health risks. Core vaccines are recommended regardless of a dog’s individual risk factors or lifestyle as they provide protection against diseases that can be transmitted to other animals or even humans.
Non-Core Vaccines for Dogs
Non-core vaccines depend on individual risk factors and lifestyle: Non-core vaccines are not universally recommended for all dogs. Factors such as a dog’s geographic location, lifestyle, and exposure risks determine a dog’s need for non-core vaccines. Non-core vaccines may protect against diseases like Lyme disease, Bordetella (kennel cough), or Leptospirosis, which are more prevalent in certain regions or environments. It is recommended to consult with your veterinarian before administering non-core vaccines to your dog.
Disease Prevention
Vaccinations are crucial in preventing dangerous diseases such as rabies, distemper, parvovirus, and hepatitis. They not only protect our dogs but also establish herd immunity, safeguarding the entire dog population from outbreaks. By vaccinating our pets, we contribute to public health by reducing the transmission of zoonotic diseases that can be passed on to humans.
Preventing Dangerous Diseases
Vaccinations play a crucial role in preventing dangerous diseases that can have severe consequences for dogs. Diseases such as rabies and hepatitis can cause significant illness, organ damage, and even death in dogs. Vaccines specifically designed for these diseases provide a reliable and effective means of protection.
Establish Herd Immunity
Vaccinating our dogs not only protects them individually but also contributes to the establishment of herd immunity within the dog population. Herd immunity occurs when a significant proportion of the population is immune to a disease, making it difficult for the disease to spread and causing outbreaks to be less likely. By vaccinating a large number of dogs, we reduce the overall risk of disease transmission and protect vulnerable individuals who may not be able to receive vaccines due to health conditions or age.
Safeguard Public Health
Vaccinating dogs against diseases that can be transmitted to humans, known as zoonotic diseases, is crucial for public health. Diseases like rabies, for example, are capable of transmitting from infected dogs to humans through bites or scratches. By vaccinating our pets against these diseases, we reduce the risk of transmission to humans, protecting not only our own health but also the health of the broader community.
Vaccine Schedule and Administration
Puppies and adult dogs require different vaccination schedules. It’s important to follow the recommended timing for boosters and have vaccinations administered by a licensed veterinarian. We’ll also discuss potential side effects to be aware of and address any concerns you may have about the vaccination process.
Vaccination Schedule
Puppies and adult dogs have different vaccination schedules. Puppies require a series of vaccinations starting at a young age to build up their immunity. They receive a series of vaccinations, usually starting around 6-8 weeks of age, with boosters given every 2-4 weeks until they reach a certain age, typically around 16 weeks. This schedule ensures that puppies receive adequate protection during their vulnerable early months. Adult dogs, on the other hand, usually receive a series of initial vaccinations as well, followed by regular boosters to maintain immunity.
Recommended Timing for Boosters
Boosters are necessary to reinforce and maintain the immune response provided by the initial vaccinations. It is important to follow the recommended timing for boosters to ensure that the dog’s immunity remains strong and effective. Delaying or missing booster shots can leave a gap in protection, potentially rendering the dog susceptible to diseases.
Potential Side Effects
While vaccinations are generally safe, like any medical intervention, they may have potential side effects. Most side effects are mild and transient, such as temporary soreness at the injection site or mild lethargy. Serious side effects are rare but can include allergic reactions or anaphylaxis. It is important to monitor your dog after vaccination and contact a veterinarian if any concerning symptoms arise.
The Benefits and Risks
Vaccinations offer numerous benefits, including reducing the severity of diseases, minimizing veterinary costs, and extending your dog’s lifespan. We’ll address common misconceptions and concerns about dog vaccinations, providing evidence-based information to alleviate worries. While vaccines do carry some risks, such as rare side effects, these risks are significantly outweighed by the benefits of disease prevention.
Reduce Severity of the Disease
Vaccinations are highly effective at reducing the severity of diseases in dogs. Even if a vaccinated dog becomes infected, the immune response triggered by the vaccine helps the body fight off the disease more effectively. This can result in milder symptoms and a faster recovery compared to unvaccinated dogs, reducing the risk of complications and long-term health issues.
Minimise Veterinary Costs
By preventing diseases through vaccinations, you can significantly minimize veterinary costs associated with treating these illnesses. Treating diseases such as parvovirus, distemper, or hepatitis can be expensive and may require intensive medical care. Vaccinating your dog, however, is a cost-effective approach to ensure their overall health and well-being, reducing the financial burden of treating preventable diseases.
Rare Risks and Side Effects
Like any medical intervention, vaccines carry some risks, albeit rare. Serious side effects are extremely uncommon, and most dogs experience only mild and transient effects, such as temporary soreness or slight lethargy. The potential risks of vaccination need to be considered in the context of the much greater risks associated with the diseases themselves. The overall benefit of disease prevention through vaccinations outweighs the minimal risk of side effects.
Staying Up to Date
To maintain optimal immunity, regular booster shots are essential. We’ll highlight the importance of keeping accurate vaccination records, ensuring you have easy access to your dog’s vaccine history.
Optimal Immunity from Regular Boosters
Regular booster shots are crucial for maintaining optimal immunity in dogs. While initial vaccinations provide a foundation of protection for your dog, it may wane over time. Booster shots help reinforce your dog’s immune response, ensuring that its immunity remains strong and effective against diseases. Without regular boosters, the level of protection may decline, leaving the dog susceptible to infections.
Accurate Vaccination Records
Keeping accurate vaccination records is essential for several reasons. Firstly, it allows you to keep track of your dog’s vaccination history, including the types of vaccines administered and the dates they were given. This information is valuable for ensuring that your dog receives the appropriate vaccines at the recommended intervals. It also serves as proof of vaccination for various purposes such as traveling, attending dog shows, or boarding facilities.
Regular Updates and Reminders
Regularly updating and reviewing your dog’s vaccination records helps you to stay on top of their healthcare needs. This includes scheduling booster shots according to the recommended timelines. Additionally, many veterinary clinics offer reminder systems, such as emails or postcards, to notify you when your dog is due for vaccinations. These reminders can be helpful in ensuring that your dog’s vaccinations are up to date.
Prioritizing vaccinations for our dogs not only protects them but also contributes to the overall health and safety of our communities. Understanding the importance of dog vaccinations empowers us as responsible pet owners to make informed decisions. Consult with your veterinarian, stay up to date on vaccines, and let’s work together to keep our dogs happy, healthy, and protected through the power of vaccinations.