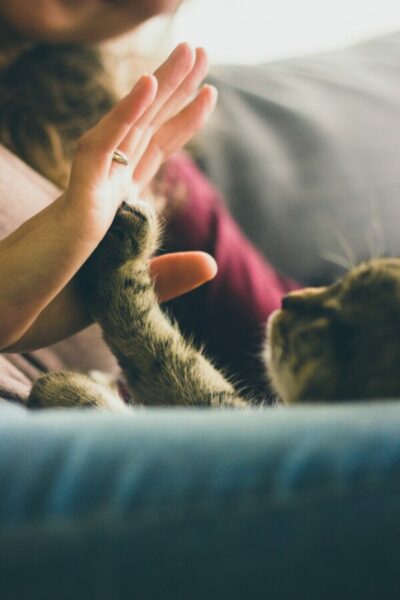
Pet therapy, also known as animal-assisted therapy, is gaining recognition as a powerful tool for improving the well-being of seniors. The companionship of pets offers numerous physical, emotional, and mental health benefits. In this article, we will explore these benefits, supported by research, and provide practical insights into how it can enhance the lives of older adults.
What is Pet Therapy?
Pet therapy involves interactions between individuals and trained animals under the guidance of a professional handler. This therapeutic approach is designed to help people recover from or cope with various health issues. For seniors, it can provide a sense of companionship, reduce loneliness, and improve overall quality of life.
Physical Health Benefits of Pet Therapy
1. Lower Blood Pressure and Heart Rate
Studies have shown that interacting with pets can help lower blood pressure and heart rate. According to a study published in the National Institutes of Health, petting a dog for just 10 minutes can significantly reduce blood pressure and stress levels in seniors.
2. Increased Physical Activity
Owning a pet, especially a dog, encourages seniors to engage in regular physical activity. Daily walks and playtime can help seniors maintain a healthy weight, improve cardiovascular health, and increase overall mobility. Research from the American Heart Association indicates that dog owners are more likely to meet recommended physical activity levels than non-owners.
3. Pain Management
Pet therapy can also aid in pain management. A study in the Pain Medicine Journal found that patients who engaged in animal-assisted therapy reported a significant reduction in pain levels. The calming presence of a therapy animal can provide distraction and comfort, helping seniors cope with chronic pain.
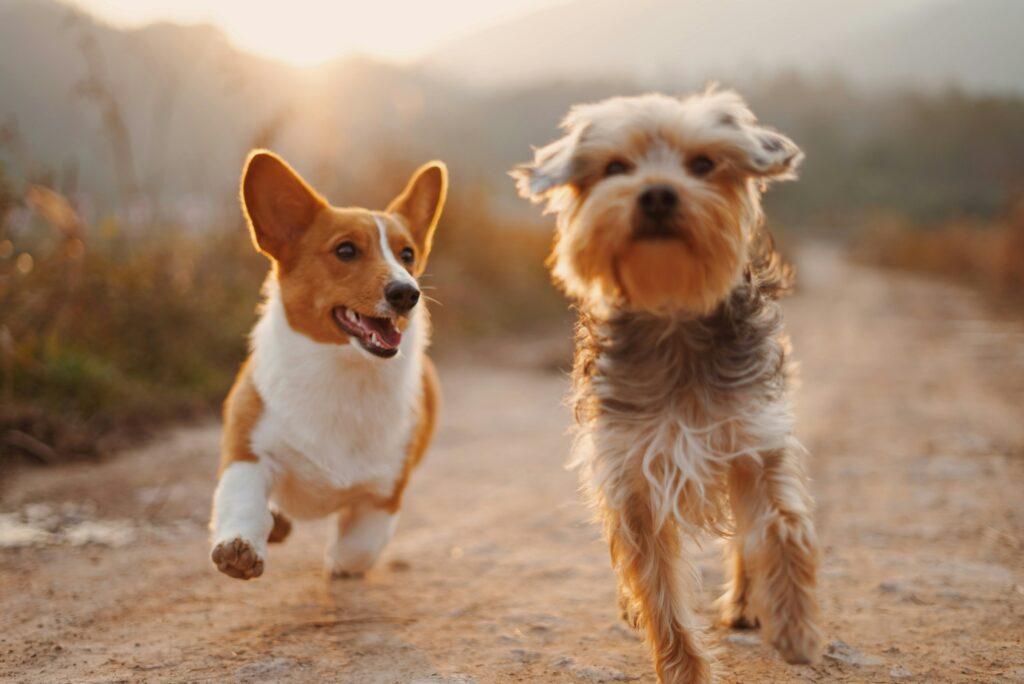

Emotional and Mental Health Benefits of Pet Therapy
1. Reduced Depression and Anxiety
Pets provide unconditional love and companionship, which can help reduce feelings of depression and anxiety. A meta-analysis published in the PubMed found that animal-assisted therapy significantly decreased symptoms of depression and anxiety in older adults. The presence of a pet can offer a sense of purpose and routine, which is crucial for mental health.
2. Enhanced Social Interaction
Pets can serve as social catalysts, helping seniors connect with others. Walking a dog or visiting a animal-assisted therapy session provides opportunities for social interaction, which is essential for combating loneliness and social isolation.
3. Behavioral and Psychological Benefits
Interacting with animals has been shown to have numerous benefits for seniors. A meta-analysis published in PubMed found that seniors with dementia who participated in animal-assisted therapy sessions experienced a significant reduction in behavioral and psychological symptoms of dementia (BPSD), particularly depression.
How to Get Started with Pet Therapy
1. Consult with Healthcare Providers
Before beginning sessions with therapy animals, it’s essential to consult with healthcare providers to ensure it’s a suitable option for the senior’s health condition. They can provide recommendations and refer you to certified pet therapy programs.
2. Find Certified Pet Therapy Programs
Look for certified pet therapy programs in your area. In Singapore, organizations like Therapy Dogs Singapore (TDS) and SOSD Singapore offer resources and directories to help you find qualified therapy animal teams.
3. Volunteer with Your Pet
If you have a friendly and well-behaved pet, consider volunteering with a pet therapy organization. Training and certification are required, but the rewards of bringing joy to seniors are immense.
Conclusion
Pet therapy offers a multitude of benefits for seniors, from improved physical health to enhanced emotional well-being. The companionship and unconditional love of a therapy animal can make a significant difference in the lives of older adults, providing comfort, reducing loneliness, and improving overall quality of life. As research continues to support the positive impact of pet therapy, more seniors can look forward to experiencing these remarkable benefits.
If you are curious to find out more about pet therapy, check out our our other posts on therapy dogs.